What is Modified Starch
Modified starch is starch that has been physically, enzymatically, or chemically altered to improve its performance in specific food applications. While natural starches (like those from corn, potato, or tapioca) work well in some cases, they often break down under high heat, extreme pH, or during long storage. Modification enhances stability, texture, and functionality, making it ideal for industries like confectionery and snack foods.
Types of Modified Starch
- Physical Modification – Heat treatment, pre-gelatinization, or moisture adjustment to improve solubility and viscosity.
- Enzymatic Modification – Use of enzymes to break down starch molecules for better control of sweetness, texture, or clarity.
- Chemical Modification – Cross-linking, oxidation, or esterification to boost resistance against heat, acid, or shear during processing.
Natural vs Modified Starch
| Feature | Natural Starch | Modified Starch |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Stability | Limited (breaks down easily) | High, withstands intense processing |
| Acid Resistance | Low | Improved for acidic formulations |
| Texture Control | Less predictable | Consistent texture and viscosity |
| Shelf Life Impact | Shorter | Extends product freshness and quality |
Common Sources for Modification
- Corn – Most widely used, cost-effective, good for multiple modification types.
- Potato – High viscosity, suitable for smooth gels and clear pastes.
- Tapioca – Neutral taste, excellent clarity, chewy texture ideal for confectionery.
- Wheat and Rice – Used for specialty textures and regional snack products.
When applied in candy fillings, coatings, or snack seasonings, these modified starches perform reliably even under tough production conditions — something natural starches can’t consistently achieve.
Importance of Modified Starch in Confectionery and Snacks

Modified starch plays a big role in making sure candies and snacks come out the way they should – from texture to shelf life. In confectionery, it’s key for controlling chewiness in gummies, preventing stickiness in candies, and keeping cream fillings stable. It also helps coatings set properly without cracking or absorbing too much moisture.
In snacks, modified starch improves crispness in chips and extruded treats, gives baked goods a consistent bite, and helps coatings stick evenly. It controls moisture so products don’t go stale too fast, keeps shapes intact during production, and boosts overall appearance.
Manufacturers in the U.S. often choose modified starch over natural starch because it performs better under high heat, acidic ingredients, and freezing or thawing. It can also handle faster production speeds without breaking down, which means fewer quality issues and less waste. That reliability, along with its versatility in different snack and candy formats, makes it a go-to ingredient for large-scale production.
Pricing of Modified Starch USD for Confectionery and Snack Food
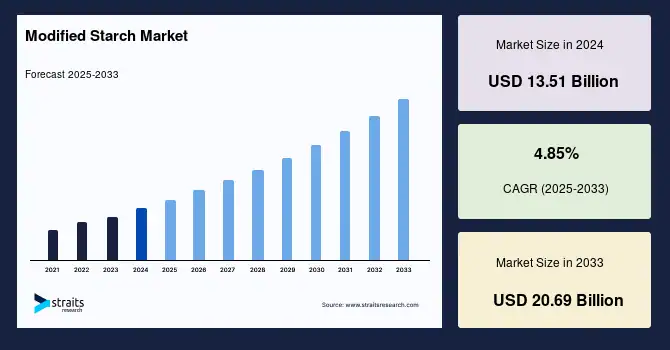
Pricing for modified starch in the confectionery and snack industry depends on several key factors. Raw material costs are one of the biggest drivers — corn, potato, and tapioca prices can change seasonally and react to global supply and demand shifts. The modification process itself (whether physical, enzymatic, or chemical) also adds cost based on energy use, technology, and production scale. Supply chain variables such as freight, storage, and import tariffs can further impact the final price you pay. Larger volume orders usually get better per‑unit rates from suppliers.
Price Range in the US Market
For U.S. buyers in 2024, food‑grade modified starch for snacks and candy typically lands in the $0.80–$1.50 per kg range (about $800–$1,500 per metric ton) depending on type, functionality, and order size. Specialty starches like E1412 (Acetylated Distarch Phosphate), E1420 (Acetylated Starch), and E1442 (Hydroxypropyl Distarch Phosphate) used in gummies, fillings, coatings, and extruded snacks can be priced toward the higher end due to their processing stability and moisture control benefits.
Regional and Market Trends
Prices can shift regionally. U.S.‑made modified starch sourced from domestic corn may avoid some of the import‑related costs of tapioca‑based starch from Asia. However, global market demand — especially from Europe and Asia — still affects pricing here. A tight potato starch supply in one region can push up U.S. costs if imports are needed.
Raw Material Cost Impact
When corn, potato, or tapioca prices spike, modified starch prices usually follow within one or two months. Manufacturers often secure contracts to smooth out short‑term volatility, but sudden droughts or trade restrictions can still cause rapid changes.
Cost Effectiveness
Compared to natural starch, modified starch can be more expensive per kg, but it’s often more cost‑effective in use. Its higher functionality reduces waste, improves product consistency, and extends shelf life — which can lower overall production costs in confectionery and snack applications.
How to Choose the Right Modified Starch for Your Products
Picking the right modified starch for confectionery and snack products comes down to knowing your product goals, testing compatibility, and working with a reliable supplier. The wrong choice can affect texture, taste, and shelf life, so it’s worth doing it right from the start.
Understand Your Product Requirements
- Texture needs: Do you need chewiness for gummies, crunch for snacks, or creaminess for a filling?
- Processing conditions: High heat, high-shear mixing, or freeze–thaw cycles may require different starch types (e.g., E1412 for stability under heat, E1420 for freeze–thaw resistance, E1442 for improved clarity and smoothness).
- Moisture control: Critical for preventing sogginess in snacks or sugar bloom in candies.
Check Compatibility With Ingredients
- Match starch type with sweeteners, fats, and acids used in your recipe.
- Some starches can handle high acid (fruit gummies), while others work best with dairy or high-fat coatings.
- Avoid starches that might react with colorants or flavorings.
Regulatory and Food Safety Considerations
- Look for FDA-compliant and food-grade certification.
- Confirm allergen-free, gluten-free, and non-GMO based on your target market.
- Check labeling requirements for E-code additives in the U.S. and for exports.
Work With a Trusted Supplier
A reliable partner like Taichy Food can help you balance performance and cost:
- Wide range of starches optimized for confectionery and snack applications.
- Consistent quality backed by international food safety standards.
- Flexible pricing—especially when ordering by volume for large-scale snack production.
Quick Reference Table – Choosing the Right Modified Starch
| Requirement | Recommended Starch Type | Key Benefit in Confectionery & Snacks |
|---|---|---|
| Heat stability | E1412 | Holds texture in high-temp cooking |
| Freeze–thaw resistance | E1420 | Prevents water separation in frozen snacks |
| Glossy & smooth texture | E1442 | Improves coating and candy appearance |
| Strong binding | Cross-linked starch | Better crispness in extruded snacks |
| Moisture retention | Acetylated starch | Keeps softness in gummies and fillings |
Taichy Foods Modified Starch Solutions for the Confectionery and Snack Series

Taichy Food offers modified starch solutions built specifically for the needs of confectionery and snack manufacturers. Their range covers both common and specialty starch types, including those ideal for gummies, chewy candies, soft fillings, and snack coatings. They work with corn, potato, and tapioca-based starches, each tailored to deliver the right texture, stability, and process tolerance needed for large-scale U.S. food production.
Product Portfolio for Snacks and Confectionery
- E1412 (Distarch Phosphate) – Great for moisture retention and freeze-thaw stability in chewy candies, gummies, and fillings.
- E1420 (Acetylated Starch) – Improves softness and shelf life, especially for baked and extruded snacks.
- E1442 (Hydroxypropyl Distarch Phosphate) – Provides excellent heat and acid resistance, perfect for high-temperature cooking in caramel, toffee, and coated snacks.
Quality and Compliance
- Follows FDA food-grade standards and meets international certifications like ISO and HACCP.
- Full traceability from raw material sourcing to final delivery.
- Consistent product performance to keep production runs efficient and predictable.
Pricing and Supply Advantages
- Flexible pricing models (per ton or per kilogram) to suit both small-scale and bulk buyers.
- Direct-from-manufacturer supply chain cuts out middle costs, keeping pricing competitive for U.S. customers.
- Steady year-round supply from multiple facilities to avoid shortages.
Customer Results
Snack brands have used Taichy’s modified starch to:
- Improve texture consistency in multi-batch candy production.
- Cut down stickiness and breakage during packaging.
- Extend shelf life without compromising flavor or mouthfeel.
- Lower ingredient costs compared to using only natural starch.
Future Trends and Innovations in Modified Starch for Snacks and Confectionery
The modified starch market for snacks and confectionery is shifting fast, driven by new tech, clean label demands, and sustainability goals. Here’s what’s shaping the future:
Emerging Technologies in Starch Modification
Manufacturers are using more advanced physical, enzymatic, and hybrid modification techniques to fine-tune starch performance.
- Controlled enzymatic breakdown for smoother texture in gummies and fillings.
- Heat-moisture treatment to improve crunch and expansion in extruded snacks.
- Cross-linked and pre-gelatinized starches for stable performance during high-temperature candy cooking.
Newer methods are allowing starches like E1412 (Distarch phosphate) and E1420 (Acetylated starch) to handle higher stress in processes without breaking down, making them a better fit for large-scale snack lines.
Health and Clean Label Trends
The U.S. consumer push for fewer additives and transparent labeling is forcing suppliers to adapt. More brands now look for:
- Gluten-free modified starch from corn, tapioca, or potato.
- Non-GMO certified options to meet retail and export requirements.
- Minimal chemical processing to support “clean label” product claims.
Many companies are exploring native starches upgraded with physical or enzymatic methods instead of traditional chemical ones to fit natural positioning.
Sustainability in Sourcing and Processing
Eco-conscious production is now a major talking point in the starch industry. Areas of focus include:
- Sourcing from sustainable crop farms that reduce pesticide and water use.
- Energy-efficient production lines for starch modification.
- Waste reduction and byproduct use in other food or industrial applications.
Suppliers like Taichy Food are already integrating these approaches into their starch portfolio, helping snack and confectionery brands meet both functional and ethical goals.